Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube: A Revolution in Today’s World
Carbon nanotubes are nano-sized cylinders and are made of carbon atoms. That means a roll of hexagonal sheet of carbon atoms if rolled, produces a carbon nanotube. Also depending on the direction in which the sheet has been rolled, different patterns of carbon nanotubes materialize.
Carbon nanotubes exhibit amazing and uncommon optical, mechanical, thermal, electrical and chemical properties, and nanowires have now been overshadowed by carbon nanotubes. Carbon nanotubes, at the individual tube level, are 200 times stronger than steel and have 5 times the elasticity of steel. They have 5 times the electrical conductivity, 1000 times the current capacity and 15 times the thermal capacity of copper.
Chemical vapor deposition, laser ablation, and arc discharge are some of the methods by which carbon nanotubes are synthesized.
Even though carbon nanotubes are all made of carbon atoms but, they can be made different from one another by aligning the atoms differently. A carbon tube can be made six times lighter than steel but hundreds of times stronger than steel with the right arrangement of the carbon atoms.
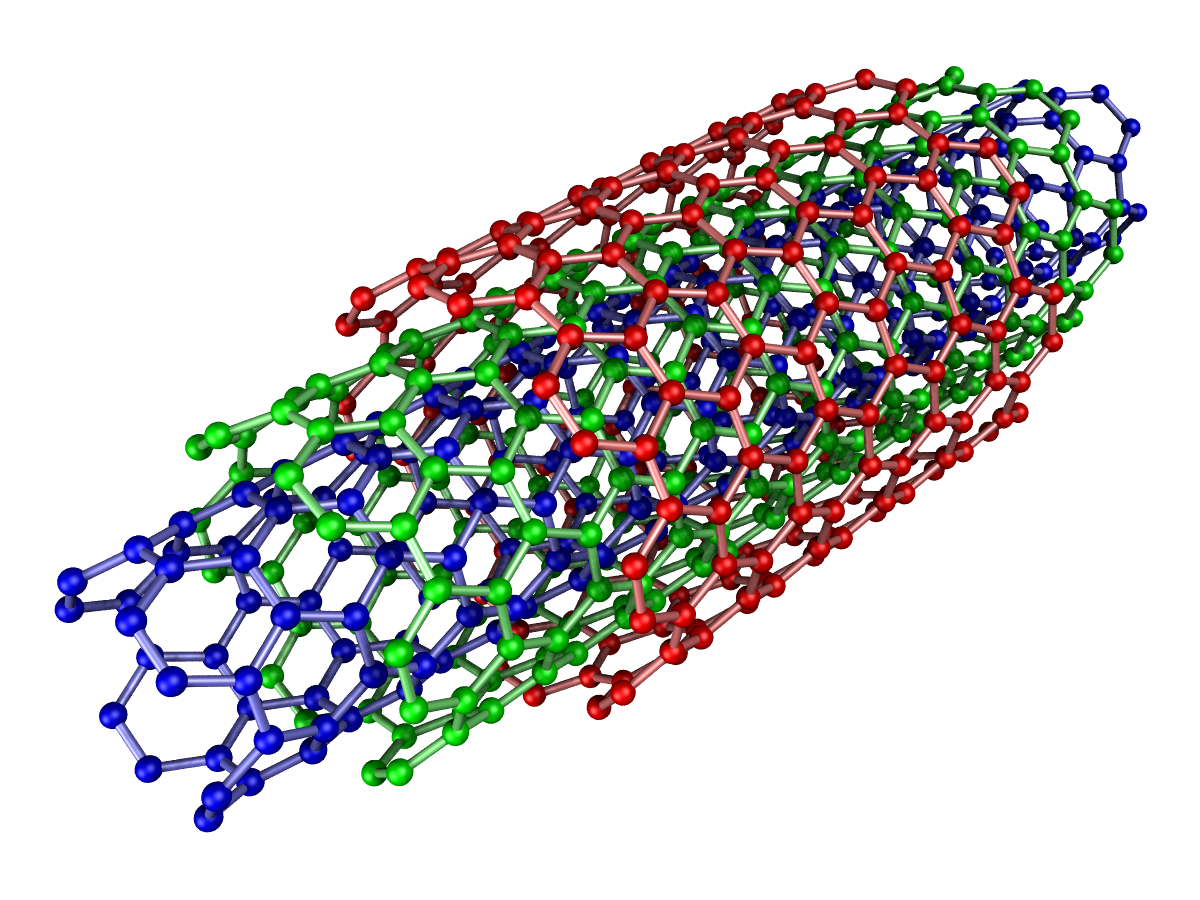
Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes: Different models
Single-walled nanotubes (SWNT) have a diameter of 1 nanometer with the length being millions of times longer. This can be visualized by wrapping a one-atom-thick-layer of graphite known as graphene into a perfect cylinder. On the other hand, multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWNT) can be visualized by multiple rolled layers or concentric tubes of graphene whose diameters range between 5 nm to 50 nm. Larger volumes of multi-walled nanotubes can be produced as compared to SWNT. But, because of its complexity, the structure of multi-walled nanotubes is understood less.
There are different models of multi-walled carbon nanotubes depending on the concentric tubes. In a Russian Model, graphite sheets are arranged in concentric cylinders – a single-walled nanotube (0, 17) arranged around another single-walled nanotube (0, . In a Parchment Model, similar to a rolled parchment or a newspaper, a single sheet of graphite is rolled into itself.
. In a Parchment Model, similar to a rolled parchment or a newspaper, a single sheet of graphite is rolled into itself.
Application of Multi Walled Nanotubes of Carbon
The applications of multi-walled carbon nanotubes are many with many more still evolving:
Their electrical conductivity property is used in automotive fuel lines, fuel hoses, fuel filler caps, IC trays, coatings and intermediate containers. Their electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding property is useful in mobile phones, housings, and Sat-Nav systems.
Due to its strength building materials, cars and aircraft parts can be made with multi-walled nanotubes that would ensure passenger safety while lighter vehicles would ensure fuel efficiency.
Due to their high mechanical strength and large specific surface, multi-walled nanotubes can be used as water filtration membranes in water filter purification to remove the heavy metals from the wastewater. Due to this property, they also find use as plastic parts for automobile fuel line components, enabling of electrostatic automobile body parts, spray paintings, and mirror housings.
As an additive in plastic industries, multi-walled nanotubes can be used for improvisation of the final product. They can also be used as additives in building materials to enhance mechanical properties.
Their strength also guarantees that they can be used to manufacture stronger medical equipment or can be used as materials for orthopedic implants. In the world of sports, multi-walled nanotubes can be used to manufacture sports equipment like hockey sticks and tennis rackets that would increase their durability without increasing their weight.
Due to its high aspect ratio and high conductivity, multi-walled carbon nanotubes find application in water processing fabrication as electrostatic discharge protection. Their thermal conductivity is used in elastomers and electronic components.
Scientists are hoping to replace transistors in microprocessors and other electronics equipment with carbon nanotubes that can also be used as semiconductors with the right arrangement of the carbon atoms.
Multi walled nanotubes, being polymers of pure carbon, can be manipulated using the chemistry of carbon to modify the structure thereby optimizing dispersion and solubility and hence, allowing ground-breaking applications in electronics, energy management, materials and chemical processing and many more.
There are different models of multi-walled carbon nanotubes depending on the concentric tubes. In a Russian Model, graphite sheets are arranged in concentric cylinders – a single-walled nanotube (0, 17) arranged around another single-walled nanotube (0,
Application of Multi Walled Nanotubes of Carbon
The applications of multi-walled carbon nanotubes are many with many more still evolving:
Their electrical conductivity property is used in automotive fuel lines, fuel hoses, fuel filler caps, IC trays, coatings and intermediate containers. Their electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding property is useful in mobile phones, housings, and Sat-Nav systems.
Due to its strength building materials, cars and aircraft parts can be made with multi-walled nanotubes that would ensure passenger safety while lighter vehicles would ensure fuel efficiency.
Due to their high mechanical strength and large specific surface, multi-walled nanotubes can be used as water filtration membranes in water filter purification to remove the heavy metals from the wastewater. Due to this property, they also find use as plastic parts for automobile fuel line components, enabling of electrostatic automobile body parts, spray paintings, and mirror housings.
As an additive in plastic industries, multi-walled nanotubes can be used for improvisation of the final product. They can also be used as additives in building materials to enhance mechanical properties.
Their strength also guarantees that they can be used to manufacture stronger medical equipment or can be used as materials for orthopedic implants. In the world of sports, multi-walled nanotubes can be used to manufacture sports equipment like hockey sticks and tennis rackets that would increase their durability without increasing their weight.
Due to its high aspect ratio and high conductivity, multi-walled carbon nanotubes find application in water processing fabrication as electrostatic discharge protection. Their thermal conductivity is used in elastomers and electronic components.
Scientists are hoping to replace transistors in microprocessors and other electronics equipment with carbon nanotubes that can also be used as semiconductors with the right arrangement of the carbon atoms.
Multi walled nanotubes, being polymers of pure carbon, can be manipulated using the chemistry of carbon to modify the structure thereby optimizing dispersion and solubility and hence, allowing ground-breaking applications in electronics, energy management, materials and chemical processing and many more.